SEO stands for Search engine optimisation. Content is fundamental to ensure that sites are performing and ranking well.
There are three main facets to SEO; accessibility, usability, and content. Accessibility allows people to find the content that they are looking for. It is important that a site is quick and easy to navigate.
It is important to have new content that is updated regularly, which represents what people are looking for.
The role of search engine is to help users find the answers to their questions. (Example, Google.com and Bing.com)
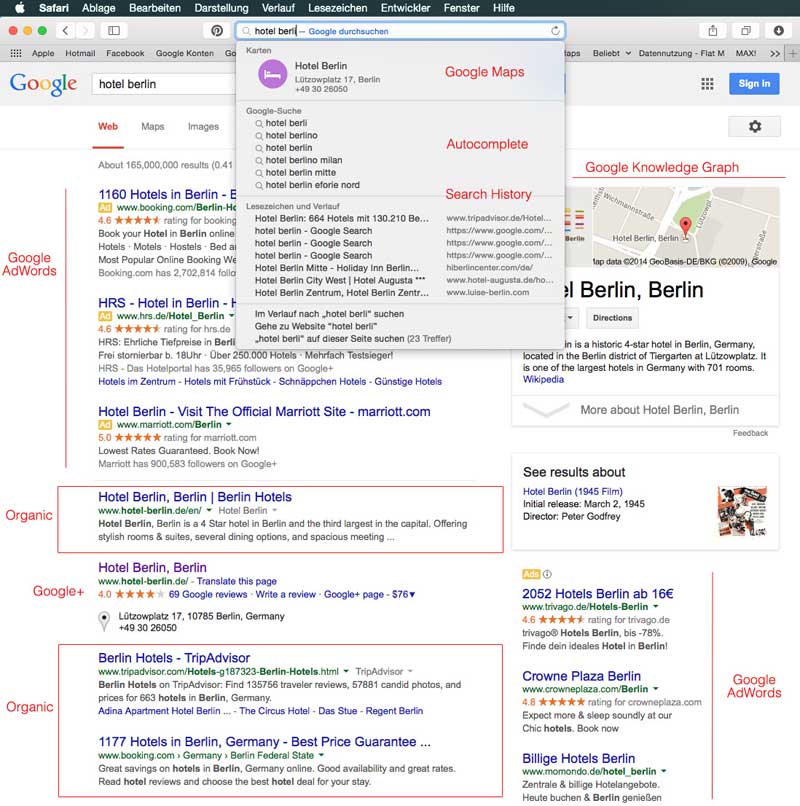
What is Search Engine Advertising?
Bing Ads are an easy to use platform that powers search ads on the Yahoo! Bing network all over the world. It features: fast and free sign-up, budgeting options, and customer targets. Same to Google Ads
Google Ads and Bing Ads are a paid search marketing program (also known as search engine marketing or search engine advertising), it serves paid adverts that match keywords which have been searched.
Google Ads/Bing Ads mean that the user sees both organic content which Google/Bing has indexed and deduced as relevant, it is also showing paid advertisements.
For example, the Yahoo Bing Network is a combined advertising marketplace made up of Yahoo, Bing, and syndicated partner sites.
The core search sites are Bing, and Yahoo. Partner sites include Facebook, WebMD, Amazon, and CNBC.
The Yahoo Bing Network is expansive, and can reach a wide audience in the U.S., where searchers spend more.
The unique searchers on the Yahoo Bing Network spend 23% more than the average internet searcher and 4.3% more than Google searchers.
The Yahoo Bing Network in the U.S. has 158 million unique searchers, 5.6 billion monthly searches, and a 29% share of the search market.
What is SERP?
Search Engine Results Page (SERP) is a list of webpages that appear in response to a keyword search in a search engine.
Crawler refers to a computer program that discovers links on the World Wide Web. Other names for crawlers are a web crawler, spider, and robot (bot). Bots are crawlers which systematically browse the web for web indexing.
Indexation is the presence or absence of a website or webpage in a search engine’s repository of pages. Ranking is the position at which a website is ranked in the search engine results page for a given keyword term or phrase.
Bingbot is the current active crawling robot discovering the majority of web content.
MSNbot is a web crawling robot that was retired in 2010, but it is still used for some media files.
Adidxbot is an ad bot for quality control.
BingPreview is for page snapshots in Bing Windows 8.
Search engines work by;
- Crawl websites,
- Index pages,
- Assign relevancy,
- Determine ranking.
Crawl websites: web crawlers/bots discover sites/pages by following links found on other sites.
Index pages: identify content structure and type (text, video, image, files) and collect relevant data about each content type.
Consider the on-page factors that determine content quality (freshness, uniqueness, keyword presence) and look at off-page signals (inbound links, and social activity).
Determine ranking: review indexed pages for relevancy signals around the keywords used in a search query, and return an appropriate SERP.
Search engines want accessibility, good user experience, and quality content. These are the powerful factors behind strong rankings.
Usually Google and Bing search engines don’t see a site in the same way that a user does, so it is important to view the site from the back-end and see what it is able to articulate from the code of the site.
Properly structuring content (headings, index tags) helps both Bing and the user to understand what is on the page. Bing doesn’t reveal the most important signals for rankings, but there are more than 1,000 signals.
There are both emerging and disappearing factors which affect rankings, these change every year.

What is Keyword Research?
Keyword research is the process of determining the keywords most likely to be used in search engines by potential website visitors.
Keyword research isn’t just about getting the most traffic to a site, it’s about getting the most relevant traffic to a site.
There are three categories that are based on the length and specificity of the keyword; head keywords, mid-tail keywords, and long-tail keywords. The length of a keyword refers to the number of words within the keywords itself.
Specificity states that the longer the keyword, the more specific the results.
Head keywords: search terms that are popular, short, and straightforward, for example ‘Microsoft Office’.
Mid-tail keywords: search terms that are very specific, long phrases that include one or more modifiers, such as ‘Microsoft Office Excel 2013’.
Long-tail keywords: keyword phrases with at least three, sometimes four or five, words in them, for example ‘Microsoft Office Excel 2013 keystroke list’.
Head keywords have more volume, and more search frequency than mid/long-tail keywords. However, the more specific the search the higher the customer quality.
Keyword phrase is a string of words where two or more are related to the same concept or topic. Keyword stemming is to return to the root or stem of the word and build additional words by adding a prefix or suffix, or by pluralizing.
Keyword basket (or bucket) is an associative grouping for related concepts, keywords, behaviours, and audience characteristics associated with the organization’s product or service.
Everything on a search engine begins with a keyword, so it is important to utilize consistent, well-planned keywords.
Click through rate (CTR) is directly related to the position a website appears on in a SERP, the higher up the page is the better.
Keyword research can be used for creating keyword lists that your content creators can use in their content writing. Keyword research can optimize your content for search engines to rank highly against a particular theme.
Keyword research can target content for promotion in social media and for ‘baiting links’ using the most effective terms. Keyword research can organize internal linking and site architecture, and choosing anchor text for internal links.
When starting keyword research, first compile as large a list as possible; and then determine which keywords are the most popular.
Identify keywords whose search engine optimisation is realistically obtainable and determine which keywords you do not want to target. Customer language is also important to identify.
There are both branded and non-branded keywords. Branded keywords are any that include your brand name, company name, trademarks, etc. Non-branded keywords are any that don’t include your brand.
Typically, your SEO efforts focus on your non-branded keywords. You can exclude your branded keywords to look at SEO effectiveness. Use search autocomplete to determine potential seed terms.
When you have a core seed list you can use the Bing keyword tool to collect the approximate search volume data for each keyword, get ideas for expanding the seed-list of terms, and get new ideas for potential keyword baskets.
When selecting keywords, there are three core areas which you should focus on; search volume, relevancy, and competition.
Search volume refers to how much opportunity there is to grow traffic for a specific keyword term.
Relevancy is how valuable a keyword is to organizational goals and objectives.
Competition tells you how hard it will likely be to rank well for a chosen keyword term.
The ideal keywords are in the cross-sections of high search volume, high relevancy, and moderate to low competition.
Kick of brainstorming by doing some high-level competitor research to see which keywords they are targeting on their web pages and in organic search; look at page titles and meta descriptions, source code, and the Bing Ads Research Tool.
Some competitors still use the meta keyword tag, and this tag can offer a wealth of information about the terms that they are targeting.
Excel is an effective way to organise your keyword research; you can use it to categorise ‘baskets’ for your keywords, and create a tab for each basket.
Use the search volume and competition data to eliminate terms on the spreadsheet that you do not want to focus on, and to isolate your target keywords.
You should remove duplicate terms, and topically irrelevant terms.
